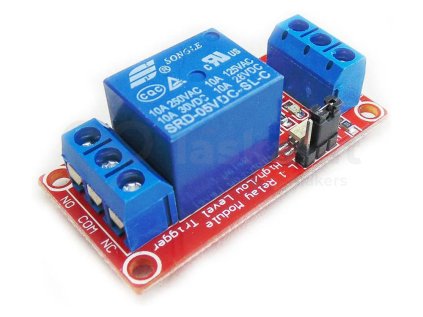
Relay Modules & MOSFET
A common relay— Switches controlled mechanically and electrically. They have the advantage of not causing a voltage drop on the switched side and generating less heat. However, they tend to be slower, noisier, and their contacts wear out more easily.
Solid State Relay (SSR) — Switches sharing similarities with common relays, but differ in that the switching is entirely managed by a semiconductor component known as a triode. SSRs have up to 100 times faster switching frequency, and the switching process is silent.
MOSFET — Similar to a standard transistor. MOSFETs are switched by voltage rather than current. Their primary advantage lies in an exceptionally fast switching frequency, facilitating PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) control of significant loads.However, they have a limited maximum switched voltage they can handle, and exhibit a higher level of heat generation. Explore MOSFET transistors further in our dedicated article.